Overview
This article highlights an important distinction for those interested in cannabis:
- THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is the psychoactive component responsible for the euphoric ‘high’ that many people associate with cannabis.
- In contrast, THCA, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is its non-psychoactive precursor.
- It requires heating to convert into THC, making it a safer option for consumers seeking therapeutic benefits without the intoxication.
Understanding this difference is crucial. Many individuals are looking for ways to manage health concerns without the risks linked to THC’s psychoactive effects. THCA may offer potential health advantages, such as anti-inflammatory properties, allowing you to explore wellness options that resonate with your needs.
Have you ever considered how cannabis might fit into your health journey? By choosing THCA, you can take informed steps toward better health while feeling supported in your choices. We invite you to explore the possibilities together, ensuring a safe and beneficial experience.
Introduction
The world of cannabis is a fascinating realm, abundant with compounds that offer a variety of effects. Among these, few are as widely discussed as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and its non-psychoactive counterpart, tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA). While THC is often celebrated for its euphoric high, THCA tends to remain largely under the radar, despite its potential therapeutic benefits.
This article seeks to explore the critical distinctions between these two cannabinoids, shedding light on their unique characteristics, effects on the body, and what they mean for consumers like you who may be seeking either recreational enjoyment or medicinal relief.
How can understanding the fundamental differences between THC and THCA empower you to make informed choices about your cannabis use? Together, let’s delve into this topic and uncover the insights that can help guide your journey.
Define THC and THCA: Key Characteristics and Functions
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the primary psychoactive substance in marijuana, well-known for creating the euphoric ‘high’ that many associate with its use. By attaching to the brain’s cannabinoid receptors, particularly the CB1 receptor, THC influences mood, perception, and cognitive abilities. For infrequent users, research shows that THC has a half-life of about 1.3 days, with metabolites detectable in urine for up to 30 days. This highlights THC’s prolonged presence in the body, which is important to consider for those exploring its effects.
On the other hand, tetrahydrocannabinolic acid is the non-psychoactive precursor to THC, primarily found in raw cannabis. This compound does not produce intoxicating sensations until it undergoes decarboxylation, a process activated by heat, such as during smoking or cooking. Understanding this transformation is vital for those seeking the psychoactive effects of THC, as its non-activated form remains inactive. Remarkably, studies indicate that 87.7% of the acidic form converts into THC when heated, emphasizing the importance of this process for effective cannabis consumption.
The difference between THC and THCA in their structural forms significantly impacts their interactions with the endocannabinoid system. While THC readily binds to CB1 receptors, the acidic form shows minimal affinity, which explains its non-psychoactive nature. This distinction, or the difference between THC and THCA, is crucial for consumers, particularly those interested in the therapeutic benefits of marijuana without the associated high. Recent research suggests that this compound may offer potential health advantages, including anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects, making it an appealing option for individuals seeking therapeutic benefits without intoxication.
For those new to marijuana, obtaining a Medical Marijuana Card through Leafy Mate can enhance access to a wider variety of products, including those with THC and THCA. With exclusive patient-only sales, larger purchase limits, and increased protections, individuals can explore various treatment options for conditions like epilepsy and chronic pain. Understanding the difference between THC and THCA is essential for making informed choices about marijuana use. As the cannabis landscape evolves, ongoing research will further illuminate the therapeutic potential of both cannabinoids, providing valuable insights for consumers and medical patients alike. It’s also important to recognize that while THC can lead to psychological dependency and ‘green out’ symptoms, its non-psychoactive counterpart offers a safer alternative for individuals wanting to avoid such risks. Together, we can navigate this journey towards informed and compassionate cannabis use.
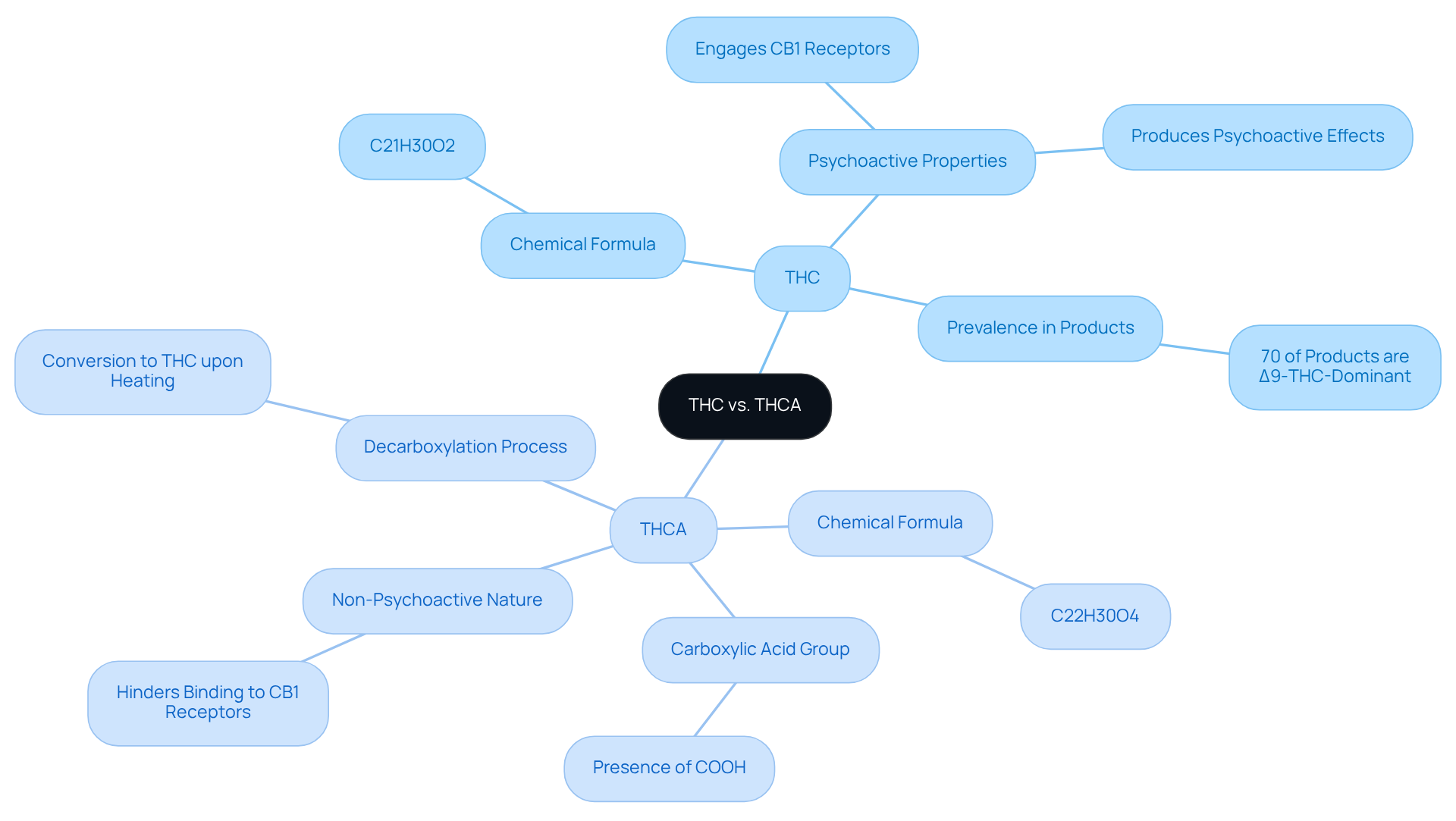
Examine Chemical Composition: THC vs. THCA
The chemical structure of THC is represented by the formula C21H30O2, while its acidic form has a more intricate structure with the formula C22H30O4. The main difference between THC and THCA lies in the presence of an additional carboxylic acid group (COOH) in THCA, which contributes to its larger size and stability in its raw form. This carboxyl group is essential as it makes tetrahydrocannabinolic acid non-psychoactive, hindering effective binding to the CB1 receptors in the brain.
Have you ever wondered how these compounds interact with our bodies? Upon heating, the carboxyl group is removed, converting the compound into THC, which can then engage with the brain’s receptors to produce psychoactive effects. This decarboxylation process is essential for users seeking the therapeutic and recreational advantages of the plant. Research suggests that the stability of THCA is greatly affected by its chemical structure, highlighting the difference between THC and THCA and the significance of comprehending these variations for informed consumption.
Significantly, studies indicate that 70% of products consumed are deemed Δ9-THC-dominant, highlighting the prevalence of THC in these products. As Melissa M. Lewis-Bakker observes, ‘Phytocannabinoids, distinctive substances generated by medicinal marijuana, engage with cannabinoid (CB) receptors to demonstrate their respective pharmacological impacts.’ Understanding these interactions is vital for consumers aiming to make informed choices in their cannabis use. Together, we can navigate this complex landscape and empower ourselves with knowledge.
Contrast Psychoactive Effects: THC’s High vs. THCA’s Non-Psychoactivity
THC is well-known for its psychoactive properties, often resulting in feelings of euphoria, relaxation, altered perception, and increased appetite. These effects arise from THC’s strong bond with CB1 receptors in the brain, leading to significant changes in mood and cognition. Conversely, there are compounds that do not produce these psychoactive sensations, making them appealing for those who wish to avoid the intoxicating ‘high’ associated with cannabis. This non-psychoactive characteristic allows for consumption in its raw form, such as through juicing or dietary supplements, potentially offering therapeutic benefits without the side effects of THC.
For example, THCA has been recognized for its anti-inflammatory properties and may assist in alleviating symptoms of conditions like arthritis and seizures. Understanding the difference between THC and THCA is essential for consumers who are seeking specific health benefits while exploring their options. With approximately 19% of Americans having tried cannabis at least once in 2021, being aware of the difference between THC and THCA can empower you to make informed choices in a rapidly evolving market. Together, let’s navigate these options with care and consideration for our health and well-being.
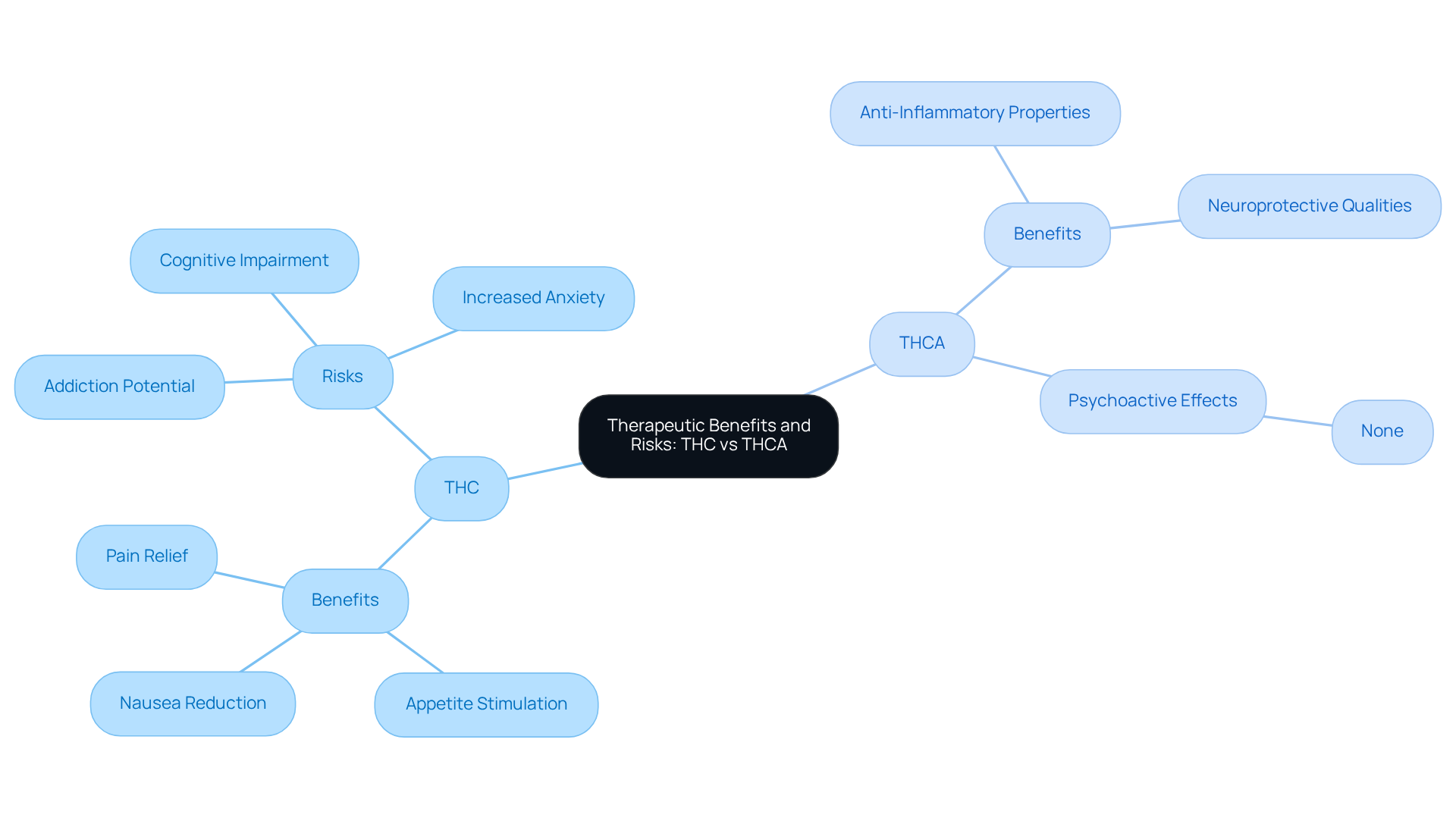
Evaluate Therapeutic Benefits and Risks: THC and THCA
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) has garnered significant attention for its therapeutic benefits, such as pain relief, appetite stimulation, and nausea reduction, especially for those undergoing chemotherapy. However, it’s important to recognize that THC use carries certain risks. It may lead to potential addiction, impaired cognitive function, and increased anxiety in some individuals. Have you considered how these factors might affect your choices?
In contrast, tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) is emerging as a promising compound, offering potential therapeutic benefits like anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective qualities. Initial research indicates that THCA may alleviate symptoms related to conditions such as arthritis and epilepsy, all without the psychoactive effects associated with THC. This could be a comforting alternative for many.
While THCA appears to have a favorable safety profile, ongoing research is crucial to fully understand its benefits and any possible side effects. As we navigate these options together, it’s essential to consider these factors carefully when evaluating the therapeutic use, especially the difference between THC and THCA. We encourage you to stay informed and explore these possibilities thoughtfully.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinction between THC and THCA is essential for anyone exploring the world of cannabis. While THC is known for its psychoactive effects and therapeutic benefits, THCA presents a non-intoxicating alternative that may also offer health advantages. This nuanced understanding empowers us to make informed choices based on our individual needs and preferences.
Throughout this article, we highlighted key points, such as the chemical differences between THC and THCA, their varying interactions with the endocannabinoid system, and the implications of their psychoactive and non-psychoactive properties. Additionally, we explored the therapeutic potential of both compounds, emphasizing the importance of understanding their respective risks and benefits.
As the cannabis landscape continues to evolve, staying informed about the differences between THC and THCA can enhance our personal health decisions and promote safer consumption practices. Whether you are seeking relief from symptoms or simply exploring cannabis for recreational use, recognizing the unique characteristics of each cannabinoid can lead to more tailored and effective experiences. Together, let’s take the next step in our cannabis journey with confidence and care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is THC and what effects does it have?
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the primary psychoactive substance in marijuana, known for creating the euphoric ‘high’ associated with its use. It influences mood, perception, and cognitive abilities by attaching to the brain’s cannabinoid receptors, particularly the CB1 receptor.
How long does THC remain detectable in the body?
For infrequent users, THC has a half-life of about 1.3 days, with its metabolites detectable in urine for up to 30 days.
What is THCA and how does it differ from THC?
Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) is the non-psychoactive precursor to THC, primarily found in raw cannabis. Unlike THC, THCA does not produce intoxicating sensations until it undergoes decarboxylation, which occurs when heat is applied, such as during smoking or cooking.
What happens to THCA when heated?
When heated, approximately 87.7% of THCA converts into THC, which is essential for those seeking the psychoactive effects of cannabis.
How do THC and THCA interact with the endocannabinoid system?
THC readily binds to CB1 receptors in the endocannabinoid system, while THCA shows minimal affinity for these receptors, explaining its non-psychoactive nature.
What potential health benefits does THCA offer?
Recent research suggests that THCA may provide potential health advantages, including anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects, making it appealing for individuals seeking therapeutic benefits without intoxication.
How can individuals access THC and THCA products?
Obtaining a Medical Marijuana Card through Leafy Mate can enhance access to a wider variety of products, including those with THC and THCA, offering exclusive patient-only sales and larger purchase limits.
What should consumers consider when choosing between THC and THCA?
Understanding the difference between THC and THCA is crucial for making informed choices about marijuana use, particularly for those interested in therapeutic benefits without the associated high or risks of psychological dependency.
Get Your Medical Card
Connect with a licensed physician online in minutes