The Cannabis Sativa plant has structural similarities to other plants; however, it is highly unique. From its’ long, slim main stem to the thick purple and green buds with orange hairs and shimmering crystals, the cannabis plant is sure to stand out among your everyday flowering plants.
Like most plants and animals, marijuana has recognizable genders with specific reproductive sex organs. Whether you’re looking to breed, grow, or both, it’s crucial to be able to tell the difference.
Can a weed plant be both male and female?
In rare breeding cases, you may end up with hermaphrodite plants that can identify male or female. These marijuana plants are equipped with both male and female traits. Regarding the cannabis plant, being labeled a hermaphrodite means it has developed male and female flowers.
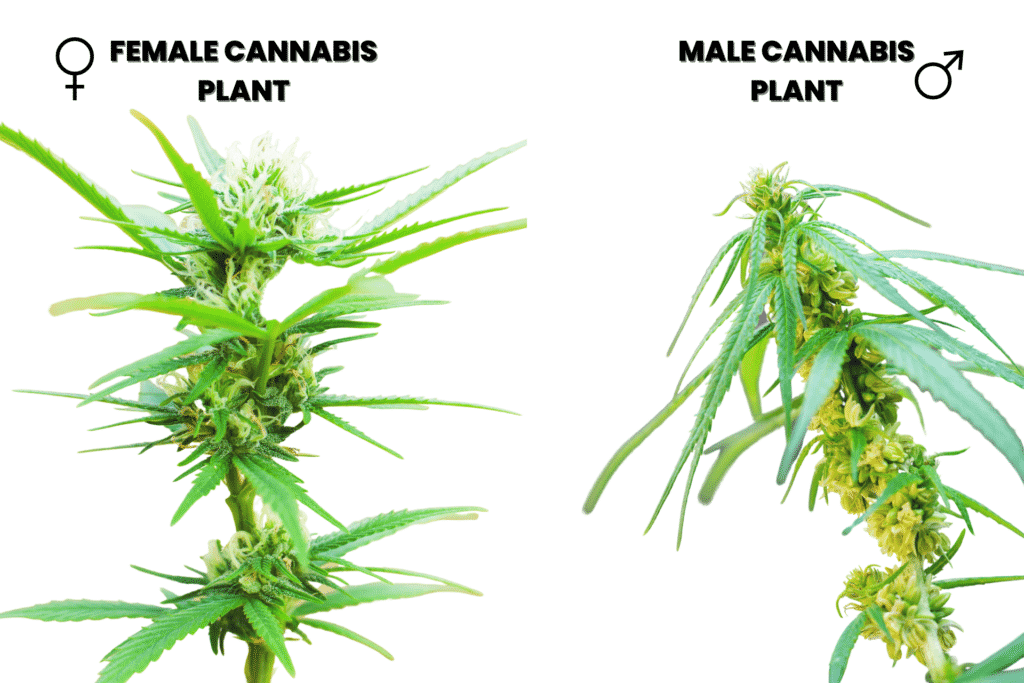
What do male and female cannabis plants look like?
Female cannabis plants take longer to show signs of their gender, but you can recognize them by the white hairs (female pistils) that appear during the flowering stage.
Male marijuana plants will have grape-like balls (pollen sacks) that appear close to the main stem where buds form on the female plant, one to two weeks after the flowering stage. The pollen sacks will often burst, and you will see them produce pollen that’s yellow on the leaves below the bursting.
Do male plants produce seeds or buds?
In short, the answer to both is no. The plant’s gender is critical when determining seed production. Male cannabis plants produce small clusters that dangle and release pollen from their pollen sacs for fertilization, while females produce flowers that will bud at harvest.
Unless a male plant turns out to be a hermaphrodite, it will not produce male seeds. The job of a male is to pollinate with pollen sacs; the position of a female is to create pre flowers and buds. Marijuana is similar to many other plants in those ways.
Is it better to grow male vs. female?
That depends on personal preference, but there are some significant distinctions between the two genders. Like humans, cannabis plants are dioecious, typically having male or female reproductive organs. However, the rare plant will have traits from both genders. Depending on the grower’s goal, it’s essential to know which one you’re working with before moving forward.
Growing male and female plants together will result in cross-pollination and thus the production of more seeds for future weed crops. But, if you’re goal is to produce large buds rich with cannabinoids, you’ll want to separate the plants.
Removing male cannabis plants will cut out fertilization of the female cannabis plants, resulting in dense, seedless buds, or sensimilla, that have a higher content of cannabinoids, such as THC or CBD. The potent, resinous buds you can find in dispensaries are sure to be from a female plant as there are no real male flowers.
What are the odds of getting a female?
Regular cannabis seeds give you a 50/50 shot at either gender. For example, if you plant six seeds, you’re likely to determine sex to be three male and three female plants.
What to do with male cannabis plants
Male plants are vital to most growers, cultivators, and farmers since they provide pollination, thus fertilizing the female plants. They can also pass down specific genes to combat poor genetics in some plants, such as mold resistance, and are vital for producing new strains or keeping the same strain you prefer.
Here are a few things you can do with your unwanted male plants:
- The male weed plant doesn’t produce a large number of cannabinoids, but it does have enough to make hash and concentrates.
- Male plants can be used for making hemp fibers as they produce a softer fiber for blankets, tablecloths, clothing, and more.
- Placing a male marijuana plant in your garden can help to repel pests and enhance soil quality. Just be sure to monitor plants that are possibly near female plants, so they don’t catch pollen from the wind.
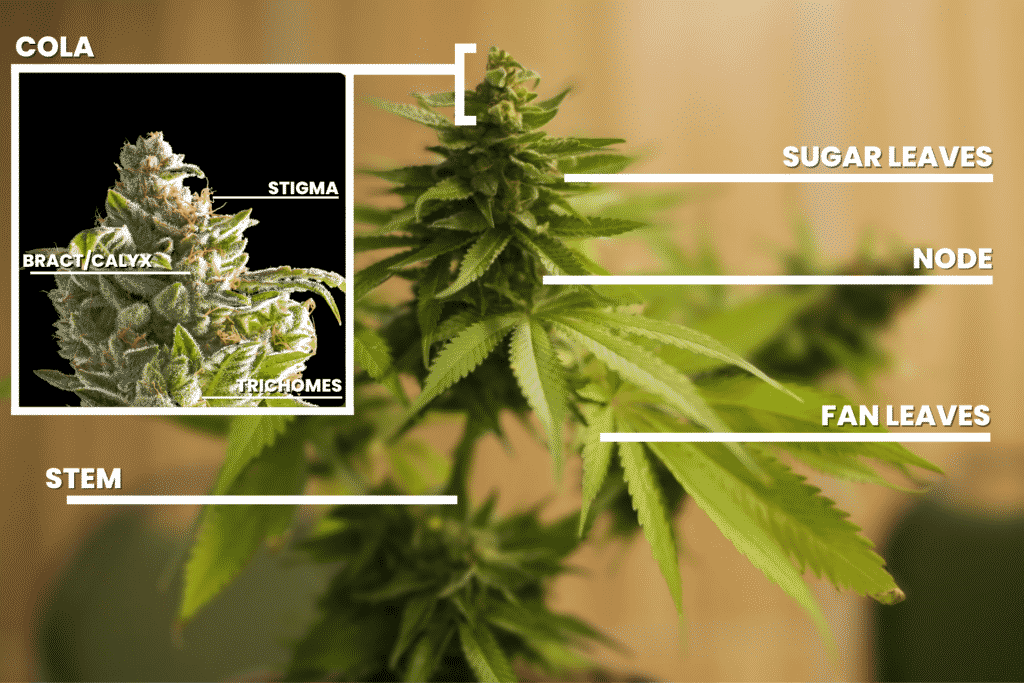
Parts of a Cannabis plant
Seeds
Female marijuana plants produce seeds and will grow fifty/fifty female or male plants. Seeds need to go through germination, sprout, and form the taproot to anchor the marijuana plant and provide stability.
Cotyledon
The cotyledon leaves are the first leaves to grow after germination. They usually grow in pairs and signify a healthy and strong female or male plant.
Roots
The roots of the female and male cannabis plant grow downward from the main stem into the soil. It’s often called a taproot. It is the lifeline of your female and male plants and will provide essential nutrients, water, and oxygen.
Branches
The branches of female and male plants grow directly out of the central stalk. They are in place to protect and support the pre flowers, buds, and fan leaves.
Stem
The main stem or stalk is the support system of the plant and grows upward from the roots. You’ll also find the pollen sacs along the stem in male cannabis plants.
Node
The marijuana plant’s node is a little “joint” where branches grow from the main stem or another branch. Some nodes contain buds, and some do not. They play an essential role while sexing cannabis but do not significantly influence potency.
Fan leaves
These leaves are large and capture light for photosynthesis. They are the iconic marijuana leaf, though they are usually discarded once trimmed due to the fact that they do not produce resin.
Sugar leaves
Sugar leaves are smaller than fan leaves and produce quite a bit of resin. These leaves are where the buds are formed and can be saved after trimming for pre-rolls, extracts, or concentrates.
Flowers
There are no male flowers; only female plants produce buds. They are small and teardrop-shaped, with pistils attached to bracts. You’ll notice shimmering trichomes, and the more, the better. The pre flower leads to flowers that contain CBD, THC cannabinoids, and terpenes. Flowers are typically dried then ground to smoke.
Cola
Cola is a cluster of flowers that form in a bunch. There will be small colas on lower branches and one large cola (apical bud) that grows at the plant’s top and the main stalk’s end. The cola is also known as the “bud site.”
Bract and Calyx
All of the female reproductive parts are together within the bract. They are tear-shaped leaves covered in resin glands that produce the highest amount of cannabinoids like CBD or THC. While you can’t see the calyx, it’s a see-through layer inside the bract over the ovule.
Stigma and pistil
In a nutshell, the pistil is the plant’s reproductive system. It contains thick strands (stigma) which look like hairs. The job of the stigma is to collect pollen, which is why they start out white and eventually turn yellow. While these reproductive parts are vital to plant growth, they do not affect potency or taste.
Trichomes
The trichomes are the tiny, sugary crystals covering and protecting the buds. They come from the glands of leaves, stems, and the calyx on male or female marijuanas plants. The more trichomes, the more potent your plant will be.
Hermaphrodite cannabis plants
The hermaphrodite plants and pre flower are rare, but they can throw a wrench in your cannabis cultivation process. They can self-pollinate, creating seeded buds and passing down the unique hermaphrodite traits.
Four main stressors can cause a cannabis plant to “herm out” :
- If the plant is being grown outdoors, it can become damaged by wind, heavy rainfall, and natural disasters. Once damaged, your marijuana plants are at risk of changing to become hermaphrodite plants.
- If the hermaphrodite cannabis plants are being grown indoors, they are at risk of being affected by temperature and light. It’s vital to keep those elements as controlled as possible.
- Like all plants, there is a slight risk of disease infection.
- Marijuana plants need specific amounts of nutrients, water, and sunlight to grow. Be sure to research the strains you are growing and know what is required.
There are two types of hermaphrodite cannabis plants:
- develops pre flower, buds, and pollen sacs at the same time
- produces visible anthers, which are pollen-producing stamen and pollen sacs
If you notice a hermaphrodite plant growing among your female cannabis plants, you’ll want to remove it immediately, just like a male plant, so that it doesn’t pollinate them. Be aware that once released by the pollen sacs, and pollen can drift miles away if you are sexing cannabis outdoors, so you will want to keep those plants as separate as space allows.
How to tell the sex in the vegetative stage
There are two methods to find the gender of cannabis plants before they begin flowering:
First, some plants produce pre flowers that are nestled between the plant’s joints. These pre flowers begin to reveal the gender between three to six weeks.
Alternatively, you can take a clone from an uncertain marijuana plant. Once the clone has rooted down, expose it to a light cycle of twelve on/twelve off to promote the flowering stage. The gender will be revealed within one to two weeks.
If there’s confusion on the gender once the flowering stage begins, look for signs that you’ve got a hermaphrodite cannabis plant on your hands. If so, take it away from your female plants immediately or risk pollination.
How to clone a cannabis plant
- Start by using sharp scissors to cut a six-inch branch from the mother plant.
- Place the branch into a rooting cube.
- Provide a top-quality growing hormone to help the clone grow.
- Once roots have started to form, transfer to a pot or the ground.
- The clone will grow its own plant with the same genetic makeup as the mother plant.
Four stages of growth tips
After seed production, it can take anywhere from three to eight months to grow weed. There are four main stages of growth for marijuana plants:
Seed Germination
The seed germination life stage can take three to ten days. You’ll want to place your seeds in a dark place that is warm and humid. Once the regular or feminized seeds open and begin to produce their first root, transfer it into a small flower pot. It will start to create the oval leaves known as cotyledons.
Seedling
Once you have a seedling, it should take approximately two to three weeks to complete this essential life stage. You’ll begin to notice serrated leaflet production, followed by larger, bladed fan leaves. Mature female cannabis plants have five to seven blades per leaf.
Vegetative stage
Next, your marijuana plants will enter into the three to sixteen weeks known as the vegetative stage. Your female marijuana plant will need at least sixteen hours of light, or six hours of direct sunlight with several hours of indirect sunlight to follow. At this stage, you’ll want to provide nutrients, water, and maintenance to your larger female cannabis plants.
Flowering stage
Finally, the flowering stage lasts eight to twelve weeks and is the final step to producing buds. This is where the twelve hours of sun twelve hours of dark come into play. If you take good care of your plants, they should begin to produce large, resinous buds with high contents of resin production. Monitoring for pre flowers should give you an idea of what your female plant buds will look like.
Plant and seedling care
When caring for a seedling, no matter the plant’s sex, be sure to keep the soil damp and moist without overwatering. We recommend misting your plant twice a day and checking the soil regularly.
If you notice any yellowing or darkening of the leaves, your female cannabis plant may have a nutrient deficiency. If so, find a high-quality “weed appropriate” fertilizer. You’ll want to watch for a few other factors: temperature, humidity, and lighting. Be sure to follow the correct steps for each life stage.
How to know your plant is ready to flower
Outdoor female cannabis plants will begin their pre flower or flowering stages once the days become shorter and the fall season approaches. Female plants will start the flowering stage for indoor growth once the light cycle has been changed to twelve on/twelve off. Once you see a wispy white hair or two, you’ll know it has begun.
Your cannabis plant will begin to form female pre flower clusters around the nodes within the first three weeks. You should notice that your plant is significantly growing in size, and its fan leaves are bright green. Around week three is the perfect time to check for disease, fungi, mold, or pests that could potentially harm your weed plant’s effort in growing flowers.
How do light periods affect cannabis life stages and gender?
When growing a cannabis plant from a bag seed, you will want to understand light periods and how they affect the cannabis life cycle. If you don’t, your plant may never produce buds. The light schedule for your cannabis plant will change throughout its life stages.
In the vegetative stage, female cannabis plants need eighteen to twenty-four hours of sunlight per day. This will help them to grow stems and leaves. Female marijuana plants will need twelve hours of light then twelve hours of complete darkness on a cycle in the flowering stage. This will promote the female plants to produce buds. Remember, there are no male flowers made from male marijuana plants.
Feminized seeds vs. Regular cannabis seeds
Regular seeds are completely organic and pure. Regular seeds, male and female, will produce the typical 50/50 male cannabis plant or female marijuana plant. Feminized seeds are extracted from a treated cannabis plant and will only result in the female plant, female pre flowers, seed production, and never male flowers.
Hydroponics, Aquaponics, and Aeroponics
There are three soilless growing techniques used for marijuana plants. With hydroponics, it instead emerges into nutrient-rich water instead of placing the plant in soil.
Aeroponics is a process used by NASA that removes moisture and soil while the roots dangle in a tank filled with top-quality, nutritious air. The plants are misted with water using this method.
Aquaponics is a combination of fish farming and the hydroponic system. In this method, most growers use their fish to supply the water with nutrients from their waste.
Growing indoors vs. outdoors
Indoor growers have ultimate control over the conditions for their female plants. You can control lighting, water intake, nutrients, temperature, and humidity if you grow weed indoors. When growing marijuana plants outdoors, not so much. With indoor growth, you don’t have to follow a particular cycle so that you can yield multiple harvests in one year.
Outdoor growers have to deal with natural elements, pests, and less control. However, growing outdoors can yield a larger, more plentiful crop. There’s also the sun, the ultimate light source at your disposal, be aware of light leaks and too much sunlight on the marijuana plants. Not to mention, outdoor growing of the female cannabis plant can save money and reduce your carbon footprint.
How to harvest your weed plants
Harvesting female marijuana plants require four main steps: cutting plants down, trimming the buds, drying, and curing the buds before smoking. If you utilize wet trimming, the process involves cutting the female flowers and then allowing them to dry. For dry trimming, you’ll remove the female plants, hang them to dry, and then cut the buds off.
An outdoor harvest in North America should happen between September and November, depending on your specific area and local climate. For indoor marijuana plants, harvesting should occur between seven and ten weeks after the flowering stage.
Common problems when growing cannabis plants
A few common issues to look out for on your female and male plants, pre flowers and buds:
- mildew
- mold
- rotting
- pH imbalance
- nitrogen deficiency
- spider mites
- algae
- nutrient burn
- light leaks
- verticillium wilt
What are the differences in growing and cultivating male and female weed plants, and how can a weed grinder affect the process?
When growing and cultivating male and female weed plants, it’s important to understand the differences in their growth patterns and care needs. Male plants are grown for breeding, while female plants produce the buds for consumption. Using a weed grinder can affect the process by breaking down the plant matter for easier consumption. For more weed grinder tips and advice, consult a professional.
Types of Cannabis plants
- Indica plants produce airy, more developed buds than Sativa. It originates from the Kush region near Afghanistan and is from a colder, mountainous climate. Indica leaves are shorter and bushy and have dark, full leaves, and clumpy buds. It has higher THC lower CBD and is known for its relaxing high. This type of weed is excellent for nighttime due to its body-high and pain-relieving effects.
- Sativa weed plants are from the warmer climates, producing tall, long leaves and dense, thick buds during the flowering stage. It has more CBD cannabinoids and less THC and is the perfect strain to consume in the morning due to its energetic, cerebral high.
- Hybrids are cross-germinated from two different strains to form a combination of Indica and Sativa. Typically, one or the other will be dominant and will, in turn, produce the effects experienced by the user. Hybrid strains are prevalent and offer a more balanced high.
- Hemp and Ruderalis are legal in the US, thanks to the Farm Bill of 2018. They are very low in THC, causing little to no psychoactive effects. Ruderalis is from Russia, is an auto-flowering plant, and has short, thin stems with large leaves. Hemp is more similar in looks to Indica and Sativa, but it doesn’t produce much THC. Hemp is used in the textile industry and for its production of alternative cannabinoids, such as CBD and CBG.
Summary
If you like to smoke buds, chances are you have been curious about male and female cannabis plant anatomy and their growth cycles. Before beginning a process of growing male and female plants, it’s crucial to look up growing laws in your state as it’s not legal everywhere.
With our guide, you should understand the basics of the female and male marijuana plant and should be able to begin your effort growing flowers for yourself. Now you will know they are certainly not the same plant depending on their sex organs.
Knowing the essential differences between male and female marijuana plants will save you time, money, and energy. From here, you can find the perfect regular or feminized seeds and begin your cannabis cultivation journey.
Get Your Medical Card
Connect with a licensed physician online in minutes












